The training of frontline operators is a key issue for industrial companies such as Michelin. It is crucial to ensure that their employees’ skills are upgraded and maintained.
On the one hand, on-the-job training with instructors is efficient but comes up against constraints of availability, access, costs… On the other hand, digital methods such as e-learning are more competitive and scalable, but not very relevant to represent the reality of the field. This is where immersive Virtual Reality training brings together the best of both worlds, to experience realistic hands-on training and to overcome physical limitations, while drastically reducing costs and training time.
It’s in this context that Michelin uses Uptale and Immersive Learning to create, deploy and analyze more than 50 immersive training courses for its frontline operators with 3 key topics: safety, production and quality.
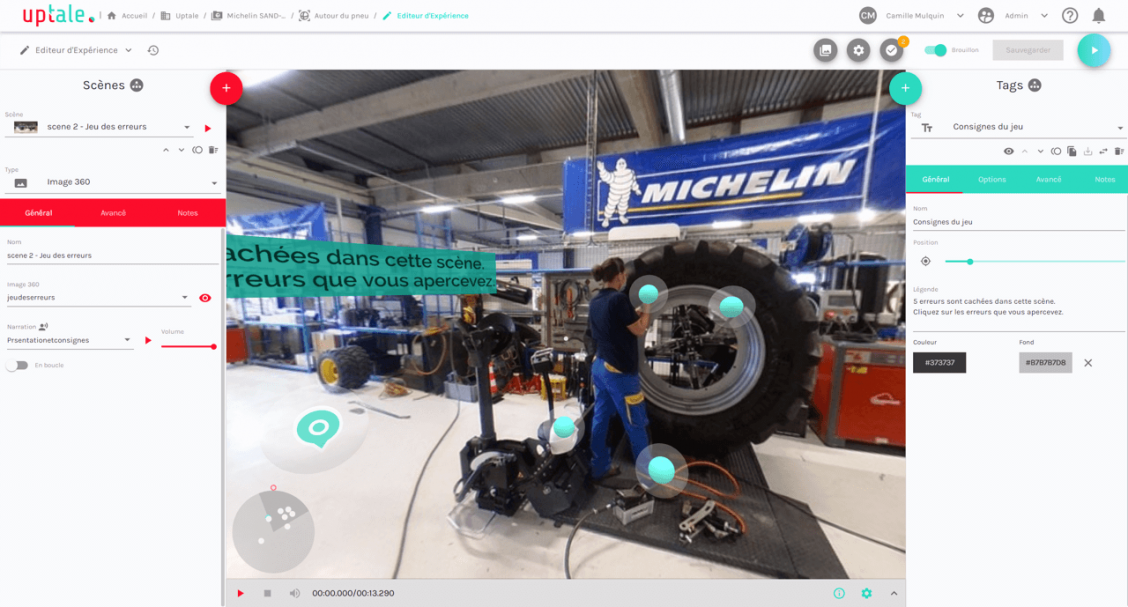
How did Michelin succeed in producing and deploying 50 VR training modules with Uptale?
Initially, a complete training course at Michelin is composed of 3 main phases (classroom training, on-the-job tutoring, and then autonomous training), says Arnaud Thébault, instructional designer at the Michelin Talent Factory, with “real problems of productivity and slowness of training”.
According to him, the immersive and digitalized field training approach requires less human and material logistics and provides “better memorization, with a gain in skills distributed over time”. He goes on to describe the Uptale tool as “a real lever of flexibility sought for digital training”.
The resources are internal with autonomous implementations and “a considerable economic advantage” compared to the possible use of external service providers. A real “universal toolbox to respond to all types of situations required in the operator training process”.
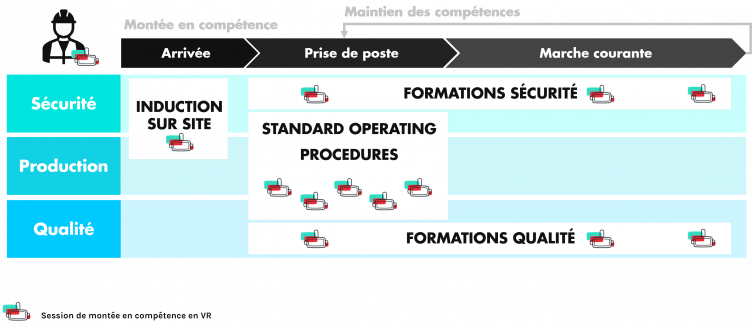
Some concrete use cases at Michelin
Their VR modules cover a range of topics such as safety, quality and production.
- Onboarding of newcomers: risk hunting, traffic rules
- Manufacturing procedures with machines and equipments
- Cardinal rules of quality
- Live a day in the shoes of a quality workshop technician
The goal: “A complete coverage of a training plan” with the support of business experts and trainers when creating the modules.
In the end, 50 training modules were created, deployed in VR and used by Michelin’s training teams at several stages of upskilling.

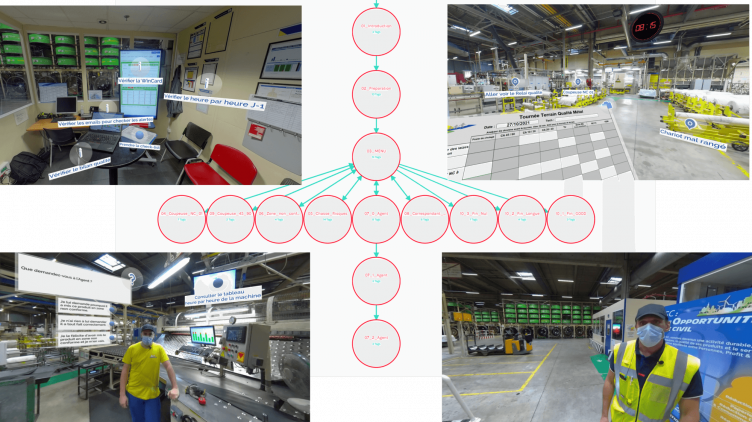
Deploying the use of VR in companies: methodology and challenges
A VR training course at Michelin is first of all a requirements document with the training needs, then three consecutive steps:
- Scripting / storyboarding
- Capture of the scenes and 360 shooting
- Editing the interactive overlay on Uptale
According to Arnaud, creating a new training course would take an average of one week at Michelin, with “factories sharing content and best practices“.
At the same time, he points out that we are facing “a moving job for the technical instructors, the monitors and the pedagogical experts“, so we really need to support them in the transformation of traianing methods. According to him, two major challenges await Michelin:
- Training in large numbers with more internal training designers
- Engaging and involving the different stakeholders of the company
Michelin's perspectives and ambitions with Uptale
Arnaud concluded on the perspectives of immersive training at Michelin:
- Deploy Uptale across the company with more and more sites willing to use the tool
- Equip each site with 360 cameras and VR headsets according to their ambitions: “between 3 and 6 Oculus Quest” per site
- Deploy more off-the-shelf training (standardized) with more professional content
- Deploy in Asia, particularly in Thailand, and then in North and South America. In particular thanks to the automatic translation feature of the modules
Great projects and great challenges await Michelin in this key industrial period.
Customer testimonial
Producing and deploying 50 autonomous VR training modules: Michelin’s challenge

